Consumers in the present and forthcoming digital era constantly demand more speed, personalization, and consistency from a brand. Generic AI models are left behind, missing out on some of these qualities, i.e., slow, excessively expensive, and perhaps out-of-place. Smart brands also recognize how optimizing LLM can really turn this promise from a tech marvel into something they bank upon.
LLM optimization isn’t mere elephantine lux; it’s tuning AI to better suit the scale, speed, or manner implicit in an aligned brand. To put more weight on what good and evil optimization means practically for you: if you use AI for speaking, chatbots, search, marketing content, or personalization…a good manager/model works for the collective good of the user and the bottom line.
Pillars of Effective LLM Optimization
- Fine-Tuning for Brand Voice
Feed your model with brand-specific content: blogs, guidelines, and customer feedback to ensure its tone is as yours. Resulting engagement is remarkably high, so we ensure that we maintain it:
A wellness brand fine-tuned its LLM on internal-content-driven optimization and saw 32% more clicks on its ad campaigns.
- Model Compression for Speed and Cost
Big models mean eyeing out cash bills and lousy UX; use techniques like quantization, distillation, or runtime optimizers such as ONNX Runtime and TensorRT to minimize the size of your model but without losing performance. This means higher churn for every spend and significantly lower cloud costs.
- Agile Prompt Engineering
Why write prompts every time? Modern brands provide templates that continuously change and adapt to suit particular audiences, seasons, or campaign types. This doubles up on quality while cutting content creation time, ensuring that the model remains updated based on trends.
Key Tools for Optimization:
- LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation): Underpins cost-efficient fine-tuning
- TensorRT &am; ONNX Runtime: Enables rapid inference

- LangChain & LlamaIndex: Bridges models with real-time data
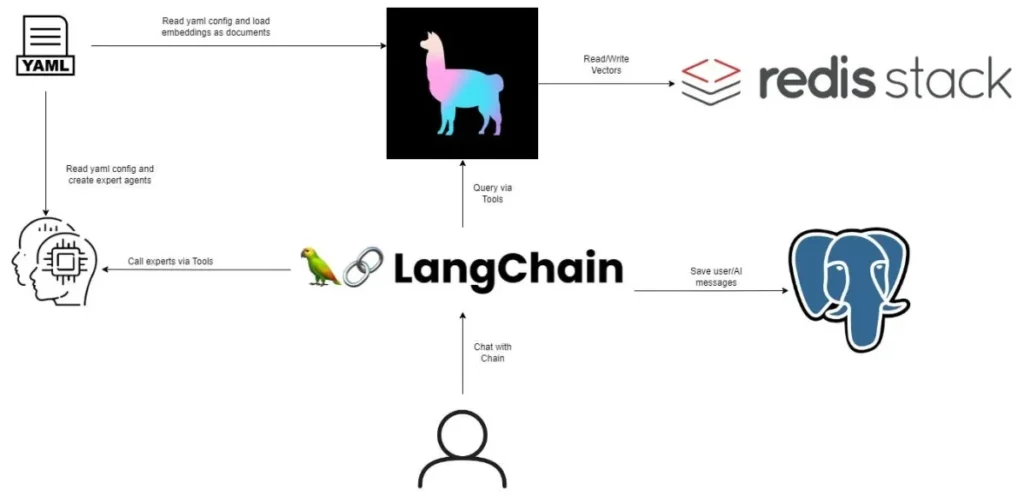
- Pinecone or Weaviate: Provides contextual memory and retrieval

Case Study: BytePlus MediaLive for Streaming
BytePlus MediaLive is targeted toward media-related and streaming brands and functions on AI platform excellence. Here is what the actual field deployments communicated:
- A streaming platform that implemented BytePlus MediaLive witnessed a 40% increase in user engagement and a 35% increase in average watch session duration
- A digital media startup was able to increase viewer engagement by 40% and decrease dropout rates 40%
- Another streaming service saw a 30% increase in engagement, and content discovery accelerated by 22% with AI-powered recommendations.
These are not just mere percentages, but actual markings of changes from a use-case vantage point; they speak volumes about what the teams can actually actualize in AI usages for media & entertainment.
Conclusion
LLM optimization isn’t the sky’s-the-limit magnitude of models; it’s just hitting the right one spot-on. After deciding upon your brand voice, devoting a couple of years to compressing for a promisingly meaningful model, and then engineering your awe-inspiring, up-keeping AI toward dynamic prompt, think of one legendary creation in which speed and intelligence come together in better paid form, e.g., your configured AI!
In this setup of the CE (customer experience)-related epic, optimization is somewhat of a shift in AI. It really kicks in; to alienate it yet further, products are built, eliciting the hearts of users, cutting costs, and branding.