In a rapidly increasing techno world, the website should be fast, usable, and user-friendly to both the users and search engines. It is the Google Lighthouse that comes into action. This free tool put out by Google helps you check the performance of your website. It’s a guiding light, a beacon that’s saying, “Here is where you’re doing well.” Or “Here is where you need improvement.”
What is Google Lighthouse?
Google Lighthouse is a tool for site auditing that creates a snapshot of a website’s performance regarding various paths. It includes performance itself, accessibility, SEO, best practices, and progressive web app activities. Its main focus audit is Google’s core web vitals. It improves web page performance and user experience (UX). It consists of three components: cumulative layout shift, initial input delay (FID), and largest contentful paint (LCP). From running the checks, it produces a report that helps the developer or owner understand what’s working and what needs fixing.
It is possible to launch Google Lighthouse as an integrated tool within Chrome DevTools. As a standalone browser plugin, or via the command line.
Areas that Google Lighthouse Covers
- Performance (Site Speed)
Lighthouse is about loading time on the site. Slow-loading sites easily send away the visitors. His decision is that he will tell how long the site takes to load and give suggestions to make it faster.
- Accessibility
It means making sure that everybody, including disabled people, will be able to visit and use your site easily. Tests involved are about color contrast, screen reader accessibility, ease of click for buttons, and so much more.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
Before Lighthouse can be ensured the possibility of easily finding and understanding by the search engine its contents as it looks into things such as meta tags, proper use of headings, and mobile-friendliness.
- Best Practices
This involves general checks for web security standards that are updated and created, using secure URLs, which resolve browser errors, and upholding coding standards.
- Progressive Web-app (PWA)
If you are developing your web app, it should also check how well it works offline and feel like a native app on mobile.
Importance of Google Lighthouse
- Improves User Experience: This implies that the sites are faster and more accessible for users.
- Enhance SEO: Good places are rated high in Google’s ratings.
- Time saver: The clear-cut and detailed suggestions aim at improvement.
- Free & Easy to Use: The Internet is available to any user without any technical skills.
Using Google Lighthouse
- Open the website in Google Chrome.
- Right-click anywhere and select Inspect.
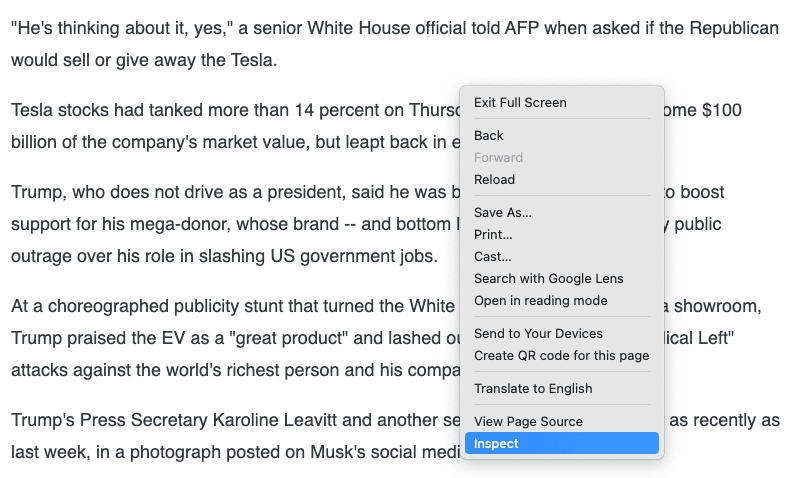
- Select the Lighthouse tab.
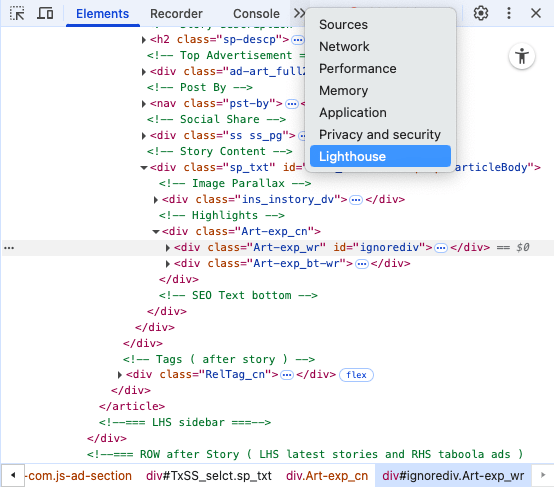
- Choose what you want to test: Performance, SEO, etc.
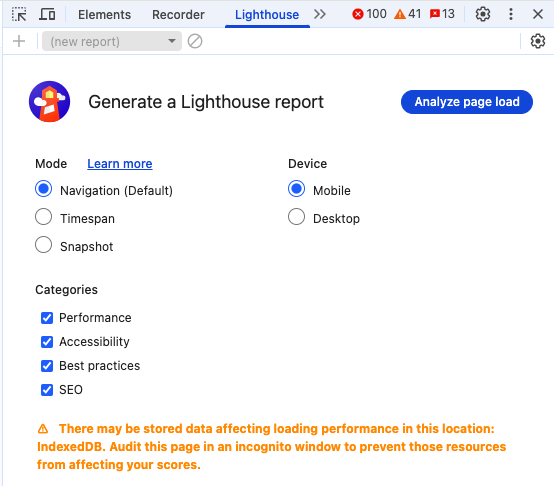
- Click on Generate Report i.e. Analyse Page Load

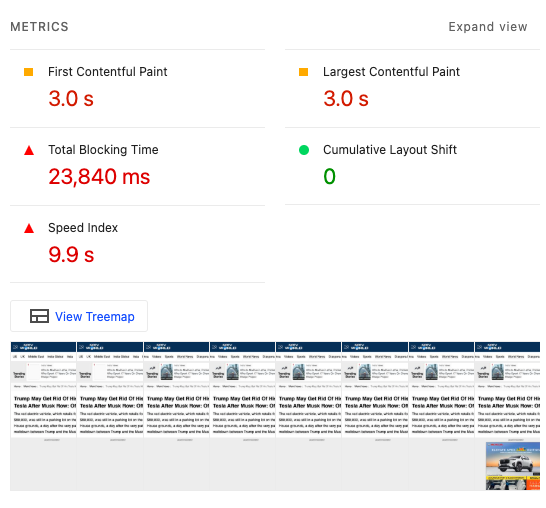
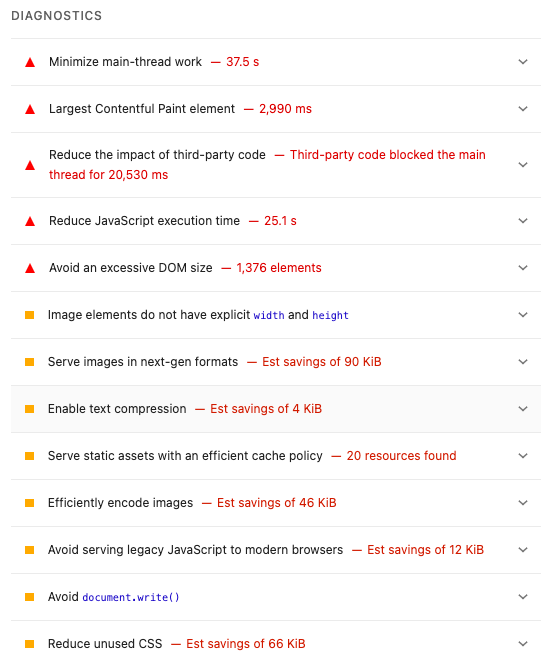
You will be given a mark out of 100 in each respective area along with useful recommendations about what needs to be fixed, as shown above.
Conclusion
It is a pretty smart but quite easy utility for the manipulations of your website to improve speed, accessibility, and search engine optimization. Whether the web developer is an entrepreneur or a blogger, Lighthouse is there to give recurrently valuable steer towards any administration of success. The Google Lighthouse appointment is similar to a health check-up for your website: it’s quick, free, and packed with useful information.

